A Visual Guide to Your Customer: What is a Customer Journey Map?
What Is Customer Journey Map
Customer journey mapping is a strategic tool that enables businesses to gain a deeper understanding of their customers' experiences and interactions across various touchpoints. By visualizing the entire customer journey from initial awareness to post-purchase support, organizations can identify key pain points, opportunities for improvement, and moments that matter most to their customers.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of a potential customer's path from the first time they become aware of your company to the point where they convert into a paying client (and ideally, beyond). It details their needs, pain points, questions, and actions across every touchpoint they have with your brand.
Why are Customer Journey Maps Important for Lead Generation?

- Understand Your Ideal Customers: Journey maps force you to delve into your target audience's mindsets, helping you tailor your messaging and marketing efforts accordingly.
- Identify Key Touchpoints: Discover where, when, and how your potential customers interact with your lead generation company. This allows you to optimize those interaction points.
- Pinpoint Friction: Uncover pain points or potential roadblocks in the customer journey. Fixing these bottlenecks directly improves conversion rates.
- Refine Your Content Strategy: Understand what information your customers need at each stage, so you can create content that provides value and moves them further down the sales funnel.
- Personalize the Experience: Journey maps allow you to personalize your approach, making the customer feel understood and increasing their likelihood of doing business with you.
Key Elements of a Lead Generation Customer Journey Map
- Buyer Persona: A detailed profile of your ideal customer.
- Touchpoints: Specific channels or moments where the customer interacts with your company (website, social media ads, email campaigns, etc.).
- Goals: What the customer is trying to achieve at each stage.
- Pain Points: Challenges or frustrations the customer might face.
- Emotions: How the customer is feeling throughout their journey.
- Key Actions: What you want your customer to do at each point (download content, schedule a demo, etc.).
Also Check: The impact of AI on the buyer's journey
Customer Journey Map Example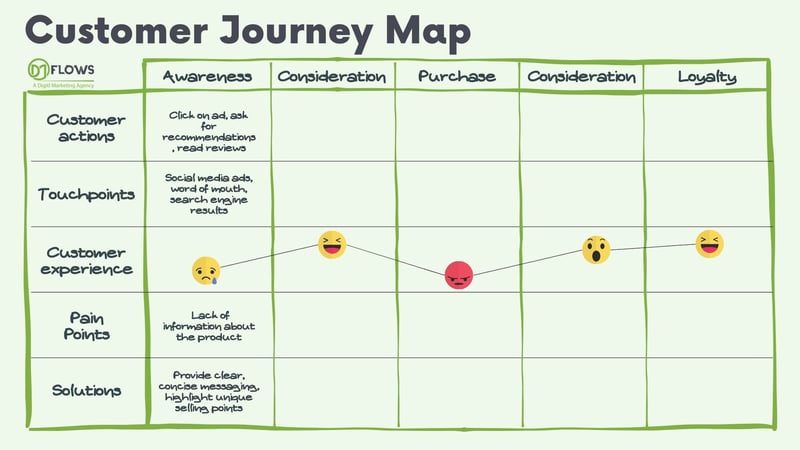
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
- Gather Data: (Surveys, website analytics, interviews, etc.).
- Define Buyer Personas: Create detailed profiles of your ideal customers.
- Outline the Stages: Map out the typical customer journey stages.
- Identify Touchpoints: List all interaction points between your company and potential customers.
- Add Customer Perspective: Detail goals, pain points, feelings, and actions at each touchpoint
- Review and Refine: Analyze for weaknesses, opportunities, and improvement areas.
Customer Journey Map Template
 5 Stages Customer Journey Map
5 Stages Customer Journey Map
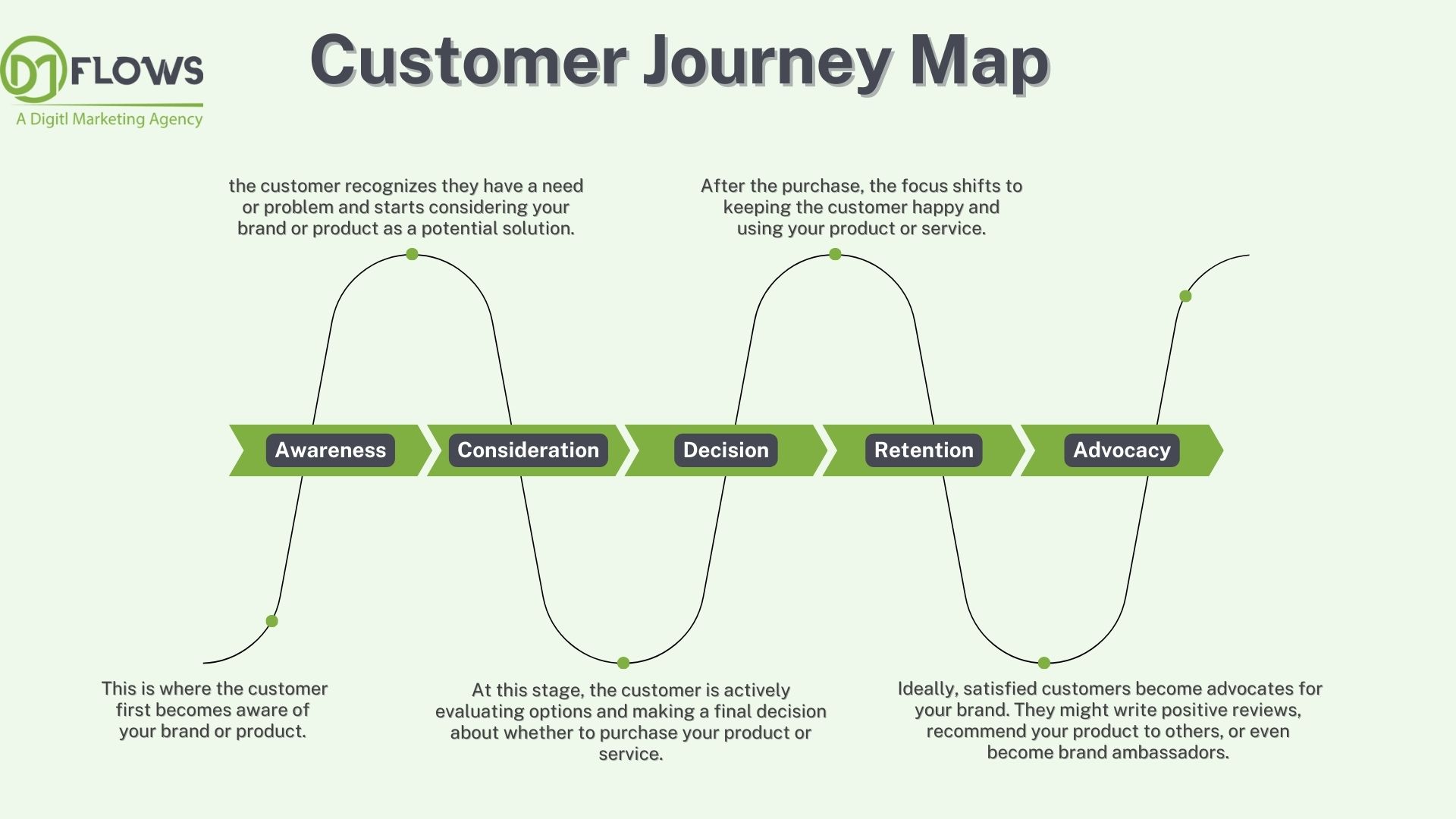
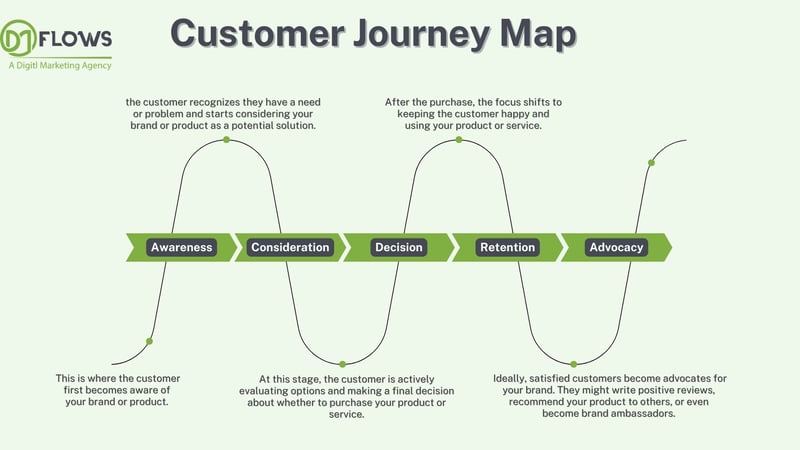
These are the 5 stages of a customer journey map outline the steps a customer takes as they interact with your brand, product, or service. While the specific names might differ slightly depending on the business, there are some generally recognized stages: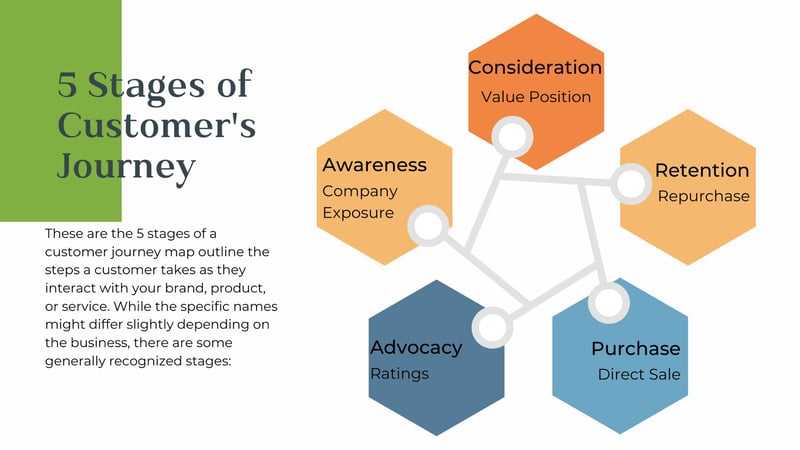
- Awareness: This is where the customer first becomes aware of your brand or product. This can happen through various channels like marketing campaigns, social media, word-of-mouth, or even just stumbling upon your website.
- Consideration: Here, the customer recognizes they have a need or problem and starts considering your brand or product as a potential solution. They might research your offering, compare it with competitors, and look for reviews or testimonials.
- Decision: At this stage, the customer is actively evaluating options and making a final decision about whether to purchase your product or service. This might involve detailed comparisons, demos, or free trials.
- Retention: After the purchase, the focus shifts to keeping the customer happy and using your product or service. This involves providing excellent customer service, offering ongoing support, and potentially additional features or products.
- Advocacy: Ideally, satisfied customers become advocates for your brand. They might write positive reviews, recommend your product to others, or even become brand ambassadors.




